Equipment and Platforms
Equipment
LabTAU is home to state-of-the-art calibration and characterization facilities for therapeutic and diagnostic ultrasound. The laboratory also homes specific research open platforms dedicated to the development of new imaging and therapeutic ultrasound strategies.
Ultrasound pressure fields hydrophone measurement motorized platforms
- 2 custom benches, 1 Precision Acoustic bench
- Ultrasound hydrophones (piezoelectric, optical)
- Hydrophone calibration bench (custom)
- Degassed water platforms (customs)
|
Custom |
UMS, Precison Acoustic |
|
FOPH 2000 (RP Acoustics) and PAFOH26 (Precision Acoustics) |
Hydrophone calibration bench (custom) |
Ultrasound radiation force balances
|
RFB-2000 (Onda) |
Optical characterization platforms
- Laser interferometer benches (e.g. vibrometry measurements transducer/biological tissue vibration modes)
- Ultrafast optical imaging (e.g. bubble cavitation dynamic)
- Spectroscopy
- Fluorescence microscopy
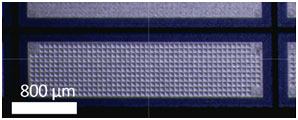
- Long working distance microscopy (e.g. microelectronic, CMUT characterization)
|
Laser interferometer (SH-140, Thales) Laser interferometer (MGL-F-532-2W, CNI) |
Ultrafast camera (Phantom, Vision Research) |
|
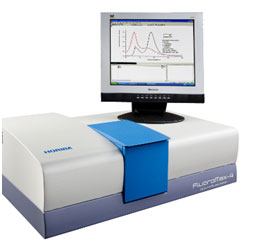
Spectro-fluorometer (Fluoro-Max4, Horiba) |
Fluorescence microcope (Eclipse Ti-S, Nikon) |
|
Long working distance microscope (CX3-2300S-V6, Omano): e.g. Zoom in of a CMUT element |
|
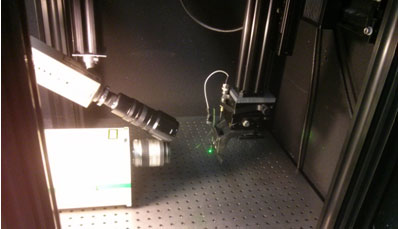
Ultrasound imaging platforms for US therapy guidance and medical diagnosis:
- 4 open research ultrasound Verasonics systems for dual-mode ultrasound (512 channels): pulsed ultrasound for imaging (e.g. ultrafast passive elastography) and LEUS therapy, continuous ultrasound for HIFU therapy
|
|
|
|
Research dual-mode ultrasound system (Vantage 256, Verasonics): US imaging + HIFU therapy. The two 256-channels systems can be synchronized to form a single 512-channel system |
|
Biological platform
- Biosafety level 2 laboratory


Animal experiment platforms
Robotic and Augmented Navigation platforms for US treatment planning:
- 3 robotic arms
- 1 optical tracking system
- 1 magnetic tracking system
|
Robotic arm (VS-050A3-AV6, DENSO) |
Augmented navigation platform including a spatial tracking system (optical: Polaris Spectra, NDI; or magnetic: Aurora, NDI) and a CE certified robotic arm (LBR iiwa, KUKA) |
Mechanical and electrical fabrication platforms :
- Workshop
- 3D-printing platforms
- Metallization system
|
Workshop |
3D-printing platforms |
|
Metallization system (E5100, Bio-Rad) |
|
LabTAU Platforms
https://www.cermep.fr/ged.php?login=vvv&catagenda=678404593d4722c&pk_orga=9&pkcateg=13 The LabTAU regularly uses CERMEP facilities for numerous work requiring heavy imaging equipment, especially (not exclusively) MRI equipment for the development of new MRgHIFUstrategies at the preclinical level. The CERMEP is a medical imaging center, where are conducted experimental and clinical research, located inside the NeuroCardiology Hospital of Lyon. Spectral scanner with photonic counting (Philips): world first installation in Lyon UMR CLB – Inserm LabTau U1032 Preclinical Research Research is organized around innovative methods and technologies. Translational research is constantly developing new tools in order to obtain increasingly reliable and fast answers to scientific questions. When the researcher reaches the limits of these tools, the use of animals remains unavoidable. In oncology, HIFU allows for focused destruction of tumours and is becoming an increasingly important part of the surgeon's therapeutic arsenal. Researchers have developed techniques to test their prototypes with computer simulations followed by experimentation on cells or living tissue. However, before these prototypes can be offered to patients, validating their safety and efficacy on relevant animal models is mandatory. For example, porcine models are often used for testing of HIFU probes intended for humans because of their relevant anatomy. A dedicated world Animal experimentation is ruled by French legislation (Decree no. 2013-118 of February 1, 2013 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes and 5 decrees) transcribed from European Directives which are regularly updated. One of the mandates of this legislation is that each project requires an authorization issued by the French Research Ministry (MESRI) after evaluation by an approved ethics committee. The French Ministry of Agriculture and Food, for its part, approves and inspects user establishments (animal facility). The world of animal experimentation operates under the umbrella of other organizations: What’s going on inside the ICE The ICE surgery laboratory is a platform created in June 2005 under the supervision of the Centre Léon Bérard (represented by Professor Michel Rivoire, ICE director) and INSERM (represented by Cyril Lafon, LabTAU director), and led by Professor Michel Rivoire. This structure also has a role in the teaching of experimental surgery and the training of future doctors: PhD and Masters student supervision, experimental surgery courses, and training on specific hardware (CHIP, laparoscopy, endoscopy etc.). The ICE also hosts several projects from LabTAU aimed at studying tumour destruction by physical agents. More specifically, novel techniques and device prototypes for tumour destruction (physical and chemical) developed by LabTAU researchers to use in surgery and radiology are tested at ICE. The ICE is also involved in other projects where surgery is needed. ICE Staff and habilitation This platform meets very precise criteria that ensure the sanitation of the premises with a logical organization of the rooms. These criteria are needed in order to maintain the accreditation of the establishment and are continuously enforced by the multidisciplinary ICE staff. The ICE is supervised by an operational manager who ensures the proper functioning of the platform (personnel planning, experimentation planning, maintenance of equipment and premises) and is assisted by other members of the ICE staff. The staff masters all techniques necessary to carry out experimental procedures, such as taking blood samples, as well as protocols required for animal care (animal facility, recognizing signs of suffering, how to fight boredom). All staff have been highly trained and have acquired theoretical knowledge via school studies, regulatory training in animal experimentation (certification), and continuous training sessions (at least 3 days over 6 years). Each technical gesture considered not to be mastered by a staff member must be performed under the supervision of a person who perfectly performs such gesture until considered trained (tutoring). Different certifications provide basic theoretical training in addition to the diploma: Animal care Animal care involves not only keeping the housing facilities clean, but also providing an environment that allows the animals to express their natural behaviour while monitoring their physical condition. Technicians are familiar with the general behaviour of animals and are capable of detecting and addressing problems. Two type of species are housed in the animal facility: rabbit and pig. ICE is equiped with: The animal facility rooms are ventilated and allow for air turnover. This system prevents the air from charging with ammonia, a component of urine. Temperature and pressure are controlled. Each animal benefits from a minimal surface area of housing as required by regulatory mandates for each species. The access to the facilities is strictly restrained. Today, some companies are specialized in supplying enrichment products. At ICE, sticks and balls are placed in rabbit housing. This kind of enrichment allows them to teethe while also being distracted. Cages are divided into several areas that allow the animal to be up high or to hide. Food is also varied as sweets and hay which are distributed daily. Concerning pigs, toys, sweets and litter are provided in the stall. The technician work involves reducing the stress of animals by spending time with them to get them accustomed to staff's presence. Socialisation also allows the animal to be distracted and to explore new smells. All animal welfare issues are discussed in the animal welfare structure, which is mandatory in each user facility. Each facility must also be linked to a veterinarian. ICE has a full-time veterinarian on site. The institute signed the French Transparency Charter edited by the GIRCOR (Groupe Interprofessionnel de Réflexion sur la Communication en Recherche) in order to promote transparency concerning the use of animals in laboratory.Cermep platforms
Primage platform (Neurosciences)
Interventional MRI platform (Neurosciences, cardiology, muscular pathologies …):
Animage platform
PET/CT platform
Radiochemistry platform
PET/MRI platform: LILI and IHU Cesame (Neurosciences, cancerology, cardiology, muscular pathologies, image sequences developments)
MEG platform (Brain)
Spectral scanner platform
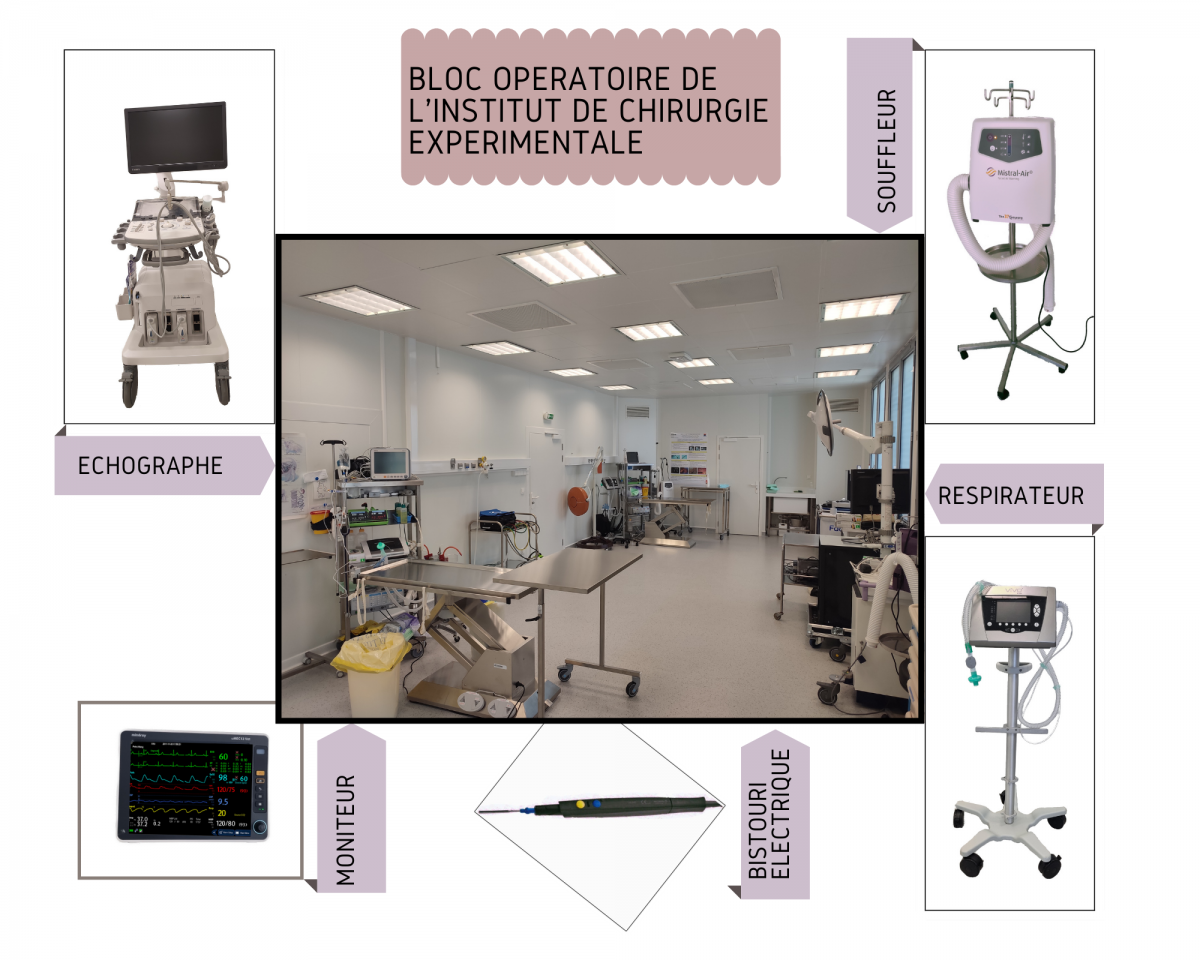
ICE Surgery Laoboratory - Experimental Surgery Institute
Its objective is to provide the environment for experimental surgery destined for oncological translational research. As a result, it congregates the LabTAU unit, a clinical unit for surgical oncology (Center Léon Bérard, Department of Surgery), the Faculty of Medicine Claude Bernard, and industrial partners.